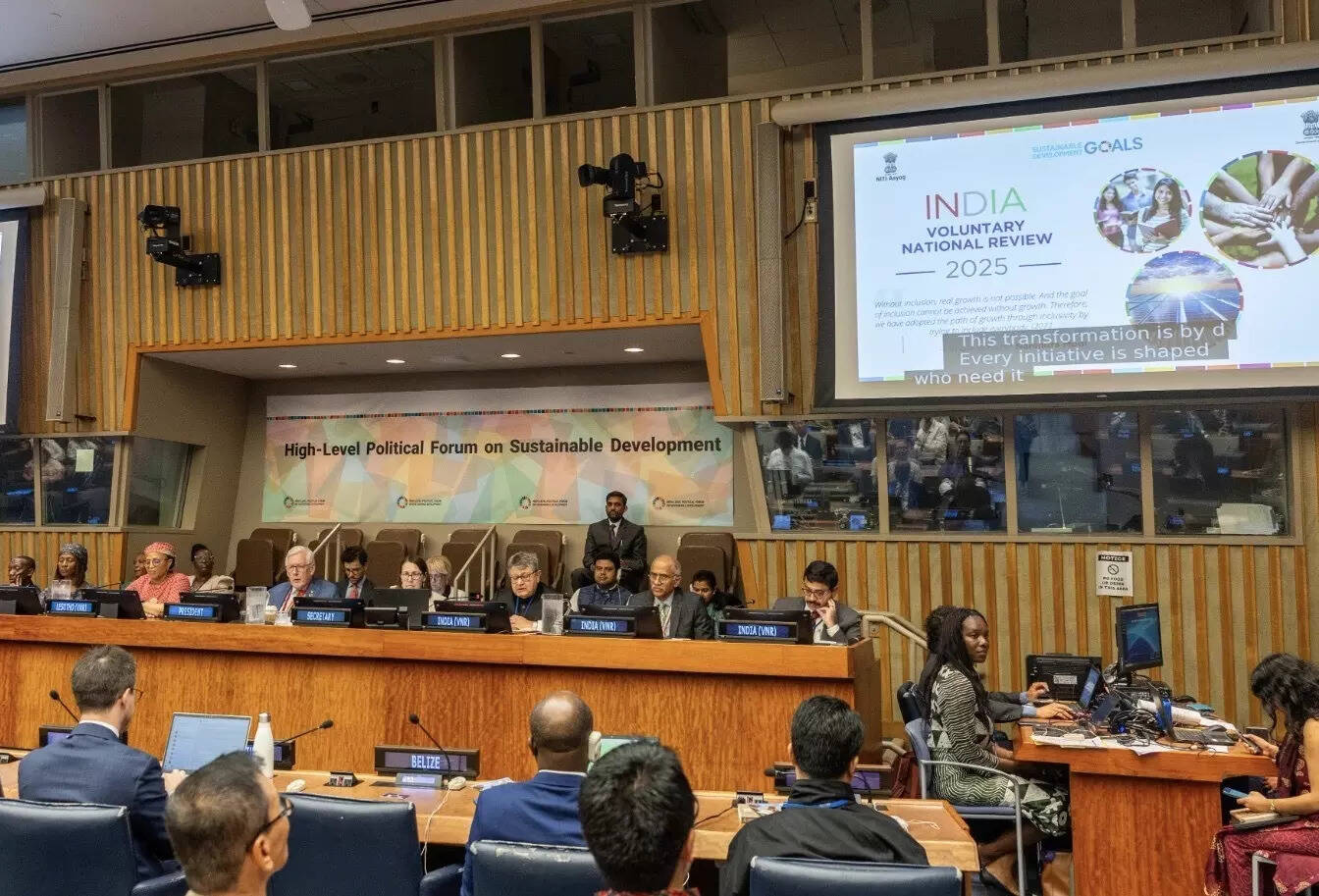
At the Ministerial Segment of the United Nations High-Level Political Forum (HLPF) on Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), held under the aegis of the UN Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC), India made a compelling case for its development journey rooted in inclusion, innovation, and institutional strength.
On July 23, 2025, Suman Bery, Vice Chairman of NITI Aayog, presented India’s Third Voluntary National Review (VNR)—a report that not only reaffirms the nation’s deep commitment to Agenda 2030 but also offers the world a view of how SDGs have become a national movement.
“This is an important opportunity to share with the world the combination of economic growth, investment in infrastructure, efficient delivery of targeted schemes, and local commitment that has transformed the SDGs into a nationwide mission,” said Bery during his address.
India’s 2025 VNR is not just a report—it is a chronicle of a decade-long transformation. Built on a whole-of-government and whole-of-society approach, the document reflects the shared energy of multiple stakeholders, including states, Union Territories, civil society organisations, development partners, and the private sector.
Coordinated by NITI Aayog through a consultative and data-driven process, the VNR highlights the importance of co-ownership and localisation in India’s SDG efforts. Notably, the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) has played a critical role in strengthening this framework through the establishment of SDG Coordination and Acceleration Centres across States and UTs.
A Decade of Transformation: Highlights from VNR 2025
India’s third VNR captures the strides made across key pillars of sustainable development, painting a picture of a country leveraging its scale, diversity, and digital might to bring inclusive growth to the forefront:
Poverty Alleviation: An estimated 248 million people have exited Multidimensional Poverty (MPI), reflecting a focused assault on deprivation across health, education, and living standards.
Food Security: Through schemes such as the PM Garib Kalyan Anna Yojana, the state ensured nutritional security for millions, especially during and after the COVID-19 pandemic.
Health and Nutrition: Initiatives like POSHAN Abhiyaan and Ayushman Bharat have deepened access to healthcare and nutritional services, especially for women and children in underserved regions.
Clean Energy Transition: With programs like the National Green Hydrogen Mission, PM-KUSUM, and the PM Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana, India is positioning itself as a global leader in the clean energy transition.
Innovation and Startups: Now the third-largest startup ecosystem globally, India is catalyzing youth-driven innovation and entrepreneurship as engines of sustainable economic growth.
Infrastructure and Industrial Policy: Initiatives such as PM Gati Shakti, Make in India, and the National Industrial Corridor Development Programme are laying down the architecture for next-generation industrial growth.
Digital Public Infrastructure: A Model for the World
One of the report’s key highlights is India’s pioneering work in building Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI). Anchored in the Jan Dhan–Aadhaar–Mobile (JAM) trinity, DPI has become a global benchmark for inclusive, transparent, and efficient service delivery.
From financial inclusion to targeted subsidies and digital identity, India’s DPI ecosystem exemplifies the transformative power of digital governance at scale.
Data for Development: Strengthening Localisation
India has significantly advanced the use of data-driven governance in its SDG implementation. Instruments like the SDG India Index, North-Eastern Region District SDG Index, and the National Multidimensional Poverty Index provide actionable metrics that guide policy interventions at both national and sub-national levels.
Moreover, India’s flagship initiatives like the Aspirational Districts Programme (ADP) and Aspirational Blocks Programme (ABP) continue to push for last-mile delivery of government services, ensuring no community is left behind.
Global Solidarity and the Viksit Bharat Vision
Beyond its borders, India is also asserting itself as a leader in South-South Cooperation, offering capacity-building, technical assistance, and institutional support to fellow developing nations. This underscores India’s growing role as a trusted development partner in the Global South.
India’s pursuit of the SDGs is firmly aligned with its long-term national vision—Viksit Bharat @2047, a roadmap to becoming a fully developed nation by the 100th anniversary of its independence. The convergence of Agenda 2030 with Viksit Bharat 2047 illustrates a uniquely Indian model of development—grounded in equity, sustainability, and strategic foresight.
As the world navigates compounding global crises, India’s Third Voluntary National Review is not just a report card—it is a blueprint of resilience, reform, and responsible governance. It invites global partners to view sustainable development not as an isolated project, but as a shared moral and strategic imperative.