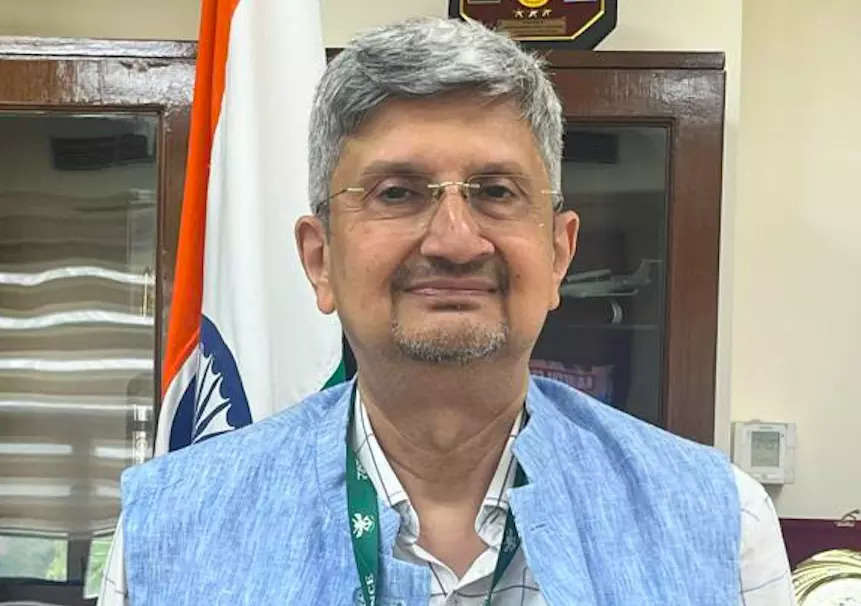
During his address at the celebration for DRDO’s 66th Foundation Day, on January 1, 2024, Dr Samir V Kamat, Secretary, Department of Defence R&D and Chairman DRDO, said that several systems developed by DRDO have been delivered, inducted or handed over to the users.
He pointed out that the Acceptance of Necessity (AoN) has been accorded this year for induction of DRDO developed systems worth more than ₹1 lakh 42 thousand crores. He noted that this was the highest ever accorded to DRDO developed systems in any year, and it constitutes a significant component of Aatmanirbharta in Defence Production. He talked about the cutting-edge defence systems that are in the final stages of testing and many that are in the phase of development trails.
Dr Samir V Kamat, in conversation with Anoop Verma, Editor (Desk), ETGovernment, sheds light on the advanced technologies and systems that the DRDO is developing to empower the defence forces and strengthen the country’s defences.
Edited excerpts:
The Defence Minister recently tweeted that defence exports have reached to the level of ₹21,083 crore in FY24, which is a growth of 32.5% over the previous fiscal. How has DRDO contributed to the development of defence systems which can be exported?
Over the years, DRDO has substantially enhanced the technological capabilities of Indian industry through various policy initiatives. We have taken initiatives like creation of an ecosystem of R&D where industry and academia work together,, Transfer of Technology (ToT), and execution of Technology Development Fund (TDF). The DRDO Patents are available on the DRDO website, and we are engaging industry and providing them support for meeting the current and future requirements of the defence sector. DRDO is promoting research by providing Grant-in-Aid funding to various Indian R&D institutions and universities.
DRDO carries out customization in the products to meet the requirements of customer countries. We provide the hand holding support and necessary policy framework to facilitate exports of defence material produced by Indian industries. In the last 5 years, DRDO developed Systems and technologies worth about Rs 10500 crore has been exported. Some of the exported systems are Hull Mounted Sonar, Torpedo Advanced Light, INDRA Radar, 3D Low Level Light Weight Radar(LLWR) Aslesha, Battle Field Surveillance Radar (BFSR), INFCOTT Software, Wargame Centre, Anti-Aircraft Simulation System A2S2, High Altitude Bio-Medical Research Centre, Weapon Location Radar, BrahMos, ATAGS and Pinaka.DRDO has been spearheading the research and production of Light Weight Tanks. How is the project progressing?
As part of Make in India initiative, Light Weight Tanks are being developed by DRDO in association with L&T. These tanks are expected to be rolled out soon. CVRDE Chennai is the nodal agency for development of this tank. Currently, the ILT (Indian Light Tank) manufacturing has been completed. The system is undergoing various internal testing for automotive, software, stabilization and other things at L&T Hazira. The ILT would be trial evaluated in summer this year. Subsequently, the vehicle would be further trial evaluated at the high altitude areas.
The main objective of the project is to develop a light tank with enhanced strategic (air portability), tactical (cruising range) and battlefield (maneuverability, low ground pressure) mobility for rapid deployment in inaccessible areas. This tank will provide a versatile platform with a high power to weight ratio, superior firepower, protection, surveillance and greater communication capabilities. The light tank possesses the lethal firepower to defeat the armour of the adversary, low flying helicopters, destroy strongholds and fortifications of the adversary.
The research and development work for Tejas Mark II has started. What are the capabilities of this fighter aircraft?
Tejas Mk 2 is an updated and more lethal version of our indigenously developed LCA Tejas, which is already operational with the Indian Air Force. LCA TEJAS MK-2 is a bigger and more capable fighter than the present LCA MK-1A one. The Mk2 variant has been designed with an eye on future wars where Beyond Visual Range (BVR) missiles will play a significant role. For air-to-air combat, it will be armed with indigenous Astra Mk 1 and Mk 2 missiles. It will have more than 80 per cent indigenous content. The IAF has accepted the comprehensive design review (CDR) of the LCA Mark 2 (Tejas) last year. The Tejas Mk-2 will be guided by the “Made in India” Uttam AESA radar, which is able to detect and block hostile electronic warfare (EW) attempts.
An efficient early warning system is the backbone of the air forces in every country. How is the DRDO Airborne Early Warning and Control System (AEW&CS) evolving to keep pace with the technologies in this area?
After successful completion of Airborne Early Warning and Control System, ‘Netra’ programme by DRDO and the capabilities and expertise developed and established through this programme has paved the way for the design, development and delivery of next-generation airborne surveillance systems such as Advanced Airborne Early Warning and Control System for the Indian Air Force (IAF). CABS, DRDO has designed and developed the Digital Airborne Active Electronically Scanned Array (DA2ESA) for primary and secondary radar for surveillance for Advanced AEW&C-MkII. The AEW&C programme has paved the way for complete self-reliance and has established capability and confidence in the country towards the entire airborne surveillance system requirement. The spin-off IFF system is another major achievement. Today, India is one of the very few countries to have achieved these capabilities.
Along with AEW&CS, DRDO has also developed the radar system called WLR Swathi which is used for locating hostile artillery. What are the capabilities of this radar?
DRDO has developed a number of radars which strengthen our defence forces in air, ground and sea. Many of the radars have been inducted into the services and some of them have been exported to friendly countries. We are completely self-reliant in the field of radars. Swathi, the weapon locating radar (WLR), is an electronically scanned phased array radar, which is capable of locating enemy guns, mortars and rockets. This radar enables troops to carry out their operational tasks without interference from the enemy and also provides them safety against enemy fire. The radar is designed to detect projectiles with small cross sections across the battlespace horizon, and has the capability to handle simultaneous fire from weapons deployed at multiple locations. It comes in two versions Swathi Plains and the Swathi Mountains.
The MPATGM missile, QRSAM missile, Agni-V, Helina missile and Astra missile are among the major missiles that DRDO has developed. What kind of success has DRDO achieved in the development of missile systems for the country’s forces?
We have achieved the goal of making India self-reliant in missiles. Many state-of-the-art missiles have been developed by DRDO. In the list of long-range missiles, there is Agni-5 which uses Multiple Independently Targetable Reentry Vehicle ( MIRV) technology. The successful conduct of this missile under the Mission Divyastra is a testament to our indigenous defence capabilities. Another big achievement was the Anti-Satellite (ASAT) missile, which successfully neutralised a satellite in space. DRDO has also demonstrated the Hypersonic air-breathing scramjet technology paving way for advanced hypersonic Vehicles. There are a number of missiles which have been indigenously developed. These include the Brahmos Extended Range Version, New generation ballistic missile ‘Agni P’, Rudram, Akash Prime Missile, Stand-Off Anti-Tank Missile, ASTRA, BVR air-to-air missile, Very Short-Range Air Defence System (VSHORADS) missile, and MPATGM.
In the area of semiconductors, India is not self-sufficient, despite the progress that the country has made in the field of software development. DRDO has a semiconductor fabrication facility. What kind of research and development in the area of semiconductors is being made in this facility?
Solid State Physics Laboratory (SSPL), the Delhi based DRDO laboratory is working in the areas of semiconductor device technologies. Semiconductor devices are used in the technological aids related to defence and space applications in addition to day-to-day consumer electronics. The laboratory works on a variety of device technologies critical to civil and defence applications. The focus is on developing device solutions with a focus on compound semiconductor device technologies for RF, photonics and IR detector applications. The laboratory pays special attention to R&D on semiconductor device technologies not available easily from outside and essential for meeting demanding strategic domestic requirements. SSPL also has a R&D fabrication facility to make designer chips. GAETEC and STARC are the pilot production FAB foundries that not only absorb the technologies developed at SSPL. The devices and circuits developed by SSPL have been implemented in a variety of defence and space missions.
What is DRDO doing to improve the nation’s cybersecurity capabilities?
DRDO contributes significantly to national security in the face of evolving cyber threats. It is focusing on cyber security and developing the software and hardware system indigenously for use by defence institutions to address the cyber security threats. The smooth functioning of critical systems is important for national defense. Cybersecurity measures in DRDO help prevent disruptions caused by cyber threats, ensuring that key defense systems such as surveillance, communication and command and control keep running smoothly.
We are working in collaboration with several academic institutions all over the country for AI based techniques to detect cyber intrusion. The large number of attacks which happen in AI ecosystems are being executed by bots. The same AI can also be used in cyber defence. We are also collaborating with friendly countries for such disruptive technologies.
DRDO has conducted certified courses in AI and Machine Learning (ML) and so far more than 1000 professionals have been trained in these domains. The organisation has come up with new learning opportunities for professionals and graduates. We have launched a new online certification in cybersecurity. Funded by DRDO, the autonomous and deemed university, Defense Institute of Advanced Technology (DIAT) is offering the course on AI and ML.
DRDO has programmes to use India’s academic talent for making valuable contributions in India’s defence sector. One of these programmes is the DRDO Industry Academia Centres of Excellence (DIA-CoEs). What is the nature and scope of this programme and what are its key achievements?
DRDO has established DRDO Industry Academia Centres of Excellence at premier academic institutions with the aim of building Directed Research Ecosystem through collaboration among DRDO laboratories, academia and startups and industries. We provide financial support through the DIA-CoE in IITs and other Universities to undertake science and technology projects and to create special tests facilities in these DRDO funded centres. Till date, more than 15 DRDO DIA-CoEs have been established. The primary aim of establishing these centres is to harness and synergize the combined strength of academia, student community, research fellows, niche technology industries and the DRDO scientists to provide impetus to research and innovations in identified futuristic defence technological domains. These DIA-CoEs will boost and sustain development of advanced technologies for future defence systems and platforms through multi-disciplinary & multi-institutional collaborative efforts. These centres will focus on making India a global leader in futuristic technologies.
DRDO has launched an MTech programme. What is the focus of this programme?
A regular MTech programme in Defence Technology was launched by DRDO jointly with AICTE to impact necessary theoretical and experimental knowledge, skill and aptitude in various defence technology areas. The programme will motivate the aspiring engineers to start their career in defence technology and will help in achieving Aatmanirbhar Bharat.